INNOVATING TODAY FOR GREENER TOMORROW
UNDERSTANDING EMBODIED CARBON
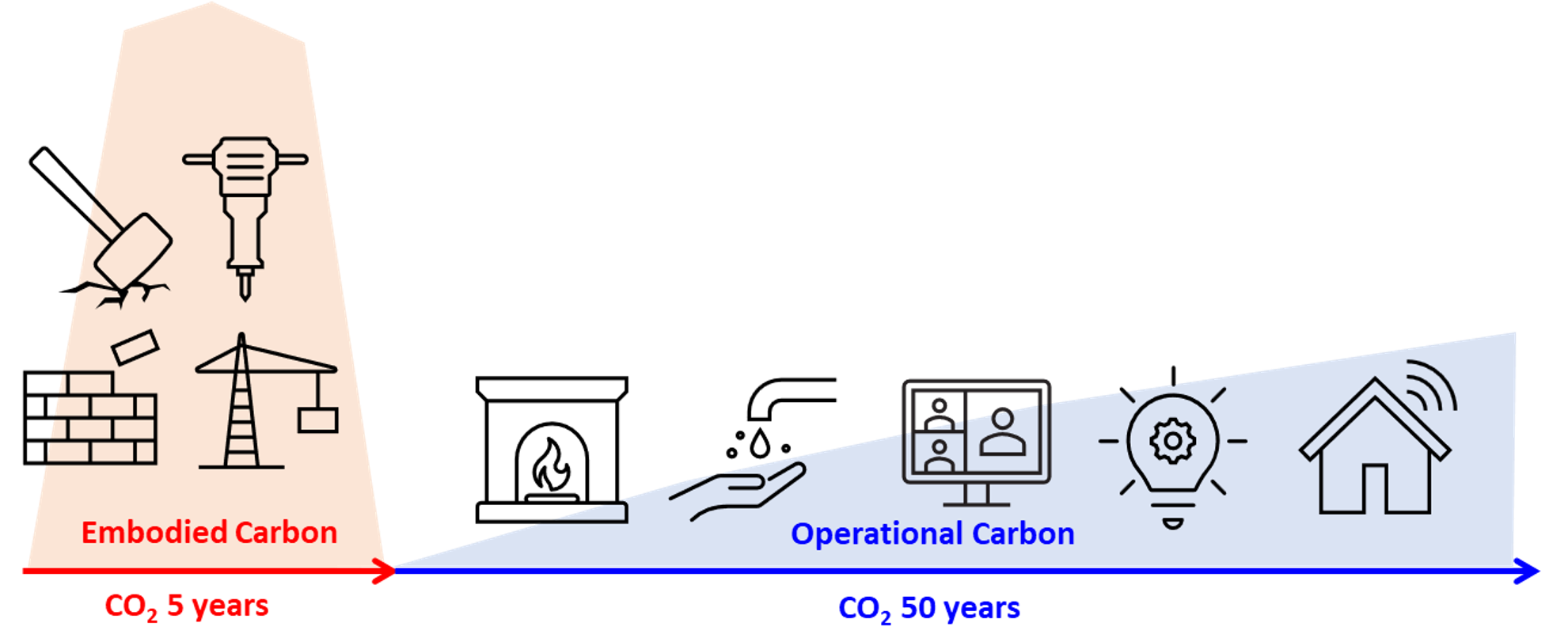
Buildings and construction account for almost 40% of energy-related carbon dioxide emissions. CO2 emissions in the buildings sector comprise two kinds: operational carbon, which arise from all energy consumed by an asset in use, over its life cycle, such as heating, lighting, and other operational activities; and embodied carbon, the emissions associated with materials and construction processes.
The embodied carbon includes:
- CO₂ emissions from material extraction, transportation to the manufacturer, and the manufacturing process itself.
- CO₂ emissions from transporting these materials to the construction site.
- CO₂ emissions from the construction activities.
In simple terms, embodied carbon represents the carbon footprint of a building or infrastructure project before it becomes operational. Additionally, it encompasses the CO₂ emissions associated with maintaining the building, as well as those produced during its demolition, waste transportation, and recycling.
While significant strides have been made in reducing operational carbon, recent data from the World Green Building Council shows that embodied carbon is increasingly accounting for a larger share of a building’s overall carbon footprint. By understanding and addressing embodied carbon, we can further reduce the environmental impact of our buildings and infrastructure, promoting more sustainable construction practices.
Total Carbon Emissions of Global New Construction from 2020-2050
WHY EMBODIED CARBON IS IMPORTANT
Embodied carbon, also known as “upfront carbon,” is the carbon dioxide (CO₂) emissions generated before a building is even occupied.
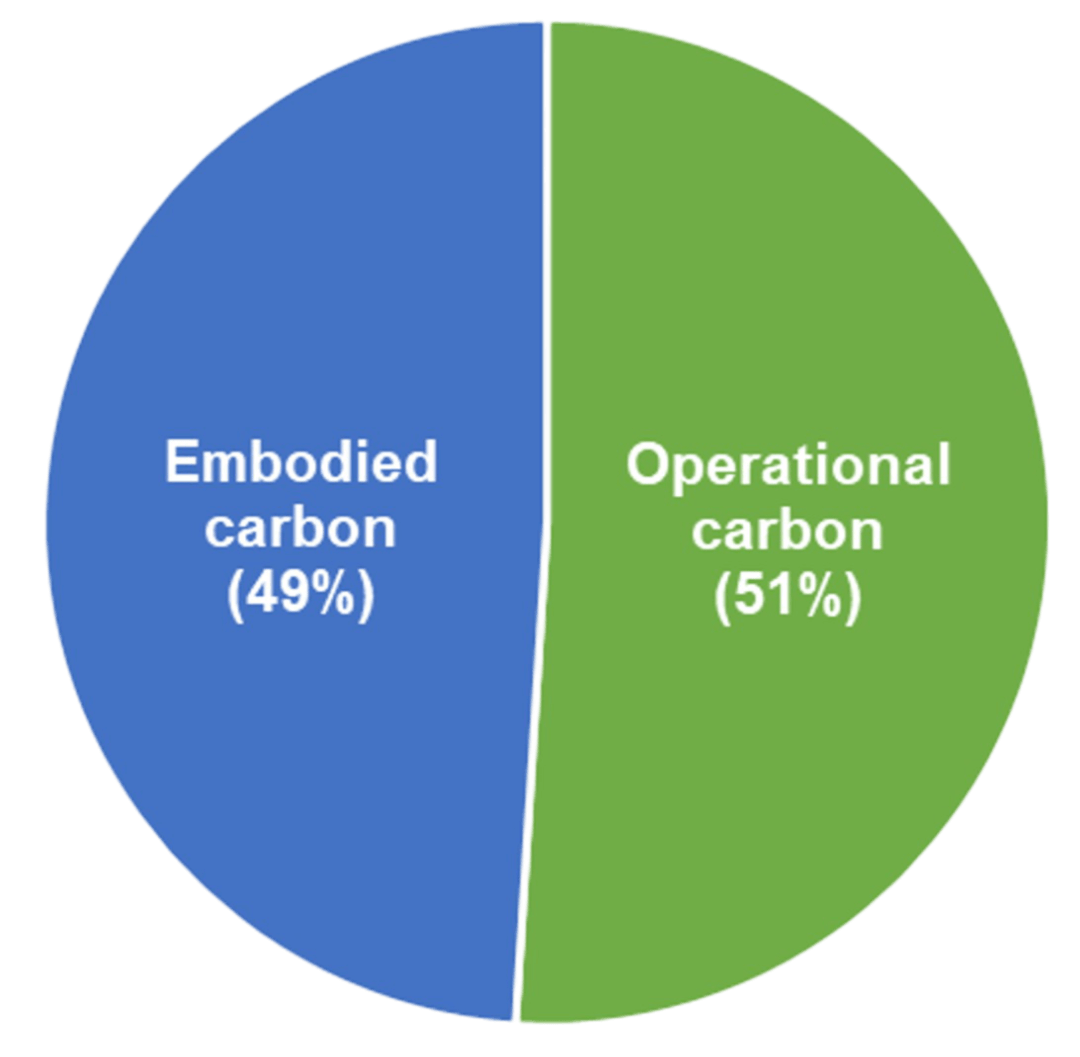
Currently, 40% of annual CO₂ emissions come from the built environment, with 13% of those emissions attributed to embodied carbon.
You might wonder, if only 13% of building emissions come from embodied carbon, why should we focus on it? The reason is that embodied carbon is released into the atmosphere now, rather than over the next 50 years. By reducing embodied carbon today, we can make a significant and immediate impact on mitigating climate change.
Furthermore, our energy grid is becoming cleaner. Over the past 50 years, the architecture, engineering, and construction (AEC) industry has made great strides in improving building energy efficiency. As a result, buildings now use less energy, and the energy they do use increasingly comes from renewable sources.
While improvements in energy efficiency have lowered operational carbon emissions, the proportion of embodied carbon is increasing. By 2050, it is estimated that nearly half of the carbon footprint of new construction will be from embodied carbon. To make a meaningful difference in the future, we must start paying more attention to embodied carbon now. Reducing embodied carbon is crucial for achieving significant and swift reductions in overall CO₂ emissions from the built environment.
TACKLING EMBODIED CARBON
Embodied carbon presents a significant challenge in the construction industry, but it also offers an opportunity for innovation and sustainability. At Karbonara, we are committed to leading the way in addressing embodied carbon and building a greener future. Here’s how we tackle this important issue:
- Material Selection: We prioritize the use of low-carbon and sustainable materials in our construction projects. By carefully selecting materials with lower embodied carbon, we can reduce the environmental impact of our buildings and infrastructure.
- Design Optimization: Our team employs innovative design strategies to minimize embodied carbon throughout the lifecycle of a project. From efficient structural systems to optimized construction techniques, we strive to maximize performance while minimizing carbon footprint.
- Lifecycle Assessment: We conduct comprehensive lifecycle assessments to quantify and understand the embodied carbon of our projects. By analyzing the environmental impact at every stage, from material extraction to end-of-life disposal, we can identify areas for improvement and implement more sustainable practices.
- Collaboration and Education: We collaborate with industry partners, research institutions, and government agencies to advance knowledge and promote best practices in sustainable construction. Through workshops, seminars, and educational initiatives, we empower stakeholders to make informed decisions and prioritize sustainability in their projects.
- Innovation and Research: We invest in research and development to explore new technologies and techniques for reducing embodied carbon. From carbon capture and utilization to innovative construction materials, we are constantly seeking innovative solutions to build a more sustainable future.
SIX TIPS TO REDUCE EMBODIED CARBON

Revive: Reuse existing buildings

Choose Wisely: Opt for low-carbon materials

Recycle: Reclaim and reuse materials

Design with Purpose: Optimise designs

Efficiency: Streamline processes and minimise waste

Innovation: Explore new technologies for sustainability
PARTNERS





